Basically, cells are of two types on the basis of the organization of DNA ( nucleus) organization of biomembranes and a variety of cytoplasmic organelles. These are prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells (Pleuropneumonia like organisms) Whereas the other organisms except the above three are included in eukaryotic cells. cell
General Organization of Prokaryotic Cells:
The prokaryotic cells are morphologically the most primitive cells. They seem to have appeared about 3.5 billion years ago. A prokaryotic cell is essentially a single membrane or one envelope system. The membrane surrounds the cell. there is no membrane enveloping the genetic material and the membranes pervading the cytoplasm are scarce, if present they are usually associated with respiration or photosynthesis.
General Organization of Eukaryotic Cells:
The Eukaryotic cells have a more elaborate internal organization than the prokaryotic cells. A eukaryotic cell is essentially a double membrane or two envelope system. The primary membrane surrounds the cell. Secondary membranes envelop the nucleus and certain other subcellular organelles, and also pervade the cytoplasm. The eukaryotic cells occur in protists, fungi, plants and animals. These organisms are called eukaryotes. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells possess some basic differences which are described in detail in the table as follows: protoplasm
Prokaryotic Cell :
- The Cell size is usually small (0.5-5.0 µm).
- A Prokaryotic cell has an envelope organization.
- The flagella, if present, are single-stranded, and without differentiation of axoneme and sheath.
- An organised nucleus is absent. Instead, a nucleoid is found.
- Cell wall, if present is absent. Instead, a nucleoid is found.
- DNA is naked, that is without an association with histones.
- DNA is usually circular.
- The amount of DNA is comparatively low.
- DNA lies freely in the cytoplasm. It is not associated with any organelle.
- The amount of DNA remains the same throughout the life cycle.
- Transcription and translation occur in the cytoplasm.
- Protein synthesis occurs only in the cytoplasm,
- Respiration enzymes are associated with the plasma membrane.
- Additional small circular DNA segments or plasmids may occur.
- The endoplasmic reticulum is absent.
- Cytoplasm does not show steaming movements.
- Ribosomes are of 70 S type.
- Mitochondria, Golgi apparatus and centrioles (Centrosome, central apparatus) are absent.
- Lysosomes and other microbodies are absent.
- True or sap vacuoles are usually absent. Instead. Gas vacuoles may be found.
- Microtubules and microfilaments are commonly absent.
- Thylakoids, if present, lie freely in the cytoplasm.
- Gametes are not formed, since sexual reproduction is absent.
- A spindle apparatus is not formed during division.
- Cell membrane may be infolded to form a complex structure called mesosome.
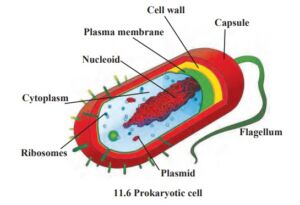
Prokaryotic Cell
Eukaryotic Cell :
- The Cell size is comparatively larger 95-100µm).
- A eukaryotic cell has two envelope organizations.
- The flagella, if present, are 11- stranded, (9+2arrangement). They show differentiation of axoneme and sheath.
- An organized nucleus is found. It is differentiated into the nuclear envelope, chromatin, one or more nucleoli, and nucleoplasm.
- Cell wall, if present, does not contain muramic acid, Nuclear DNA is associated with histone proteins.
- Nuclear DNA- Linear. Extranuclear DNA- Circular.
- The amount of DNA is Comparatively very high.
- Most of the cell DNA lies in the nucleus. A small quantity is also found in the plastid and mitochondria.
- The amount of DNA Shows a regular alternation between diploid stages.
- Transcription occurs in the nucleus while translation takes place in the cytoplasm,
- Protein synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm as well as mitochondria and plastids.
- Respiratory enzymes are present in both cytoplasms as well as mitochondria and plastids.
- Plasmids are usually absent.
- The cytoplasm is differentiated into the cytoplasmic matrix and endoplasmic reticulum.
- Cytoplasm usually shows streaming movements.
- Ribosomes are 80s type. 70s ribosomes however occur in plastids and mitochondria.
- Mitochondria and Golgi apparatus are usually present. Centrioles are usually present in animal cells.
- True or sap vacuoles are commonly found.
- Microtubules and microfilaments are important constituents of eukaryotic cells.
- Thylakoids, if present, are grouped inside the chloroplasts.
- Gametes are formed either directly or through meiosis, as sexual reproduction is found in the life cycle.
- A spindle apparatus is produced during nuclear division.
- Mesosome-like Structures are absent.
- The eukaryotic cells are of two types- plant and animal cells. Most of the organelles and other structures of cells are common to animals and plants.
Conclusion: This is basic but important information for all biological students. I hope it will improve your knowledge.
Share it with your friends and classmates, Stay connected.
- Read More 👉🏻 cell
- Read More 👉🏻 types-of-cell
- Read More 👉🏻 protoplasm
- Read More 👉🏻 gravitation





 Total Users : 8535
Total Users : 8535
















Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.